Diagnostic radiographer
A diagnostic radiographer is a registered healthcare professional who uses imaging technology including X-rays, CT and MRI machines to create images of the inside of the human body for the diagnosis and treatment of illness and injury. They operate sophisticated equipment, position patients, produce images of high diagnostic quality and provide patient care throughout imaging procedures. You will find radiographers working in hospitals and specialist clinics. Some specialise in specific areas, like breast screening (mammography) or ultrasound (sonography). They are also key members of the wider healthcare team and can progress into more advanced roles with extra training. Career progression can lead to Enhanced or Advanced practice after completing a post-graduate qualification.
Becoming a radiographer involves completing a BSc undergraduate degree or degree apprenticeship. Once qualified you will register with the Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC).
For further information, visit:
NHS Careers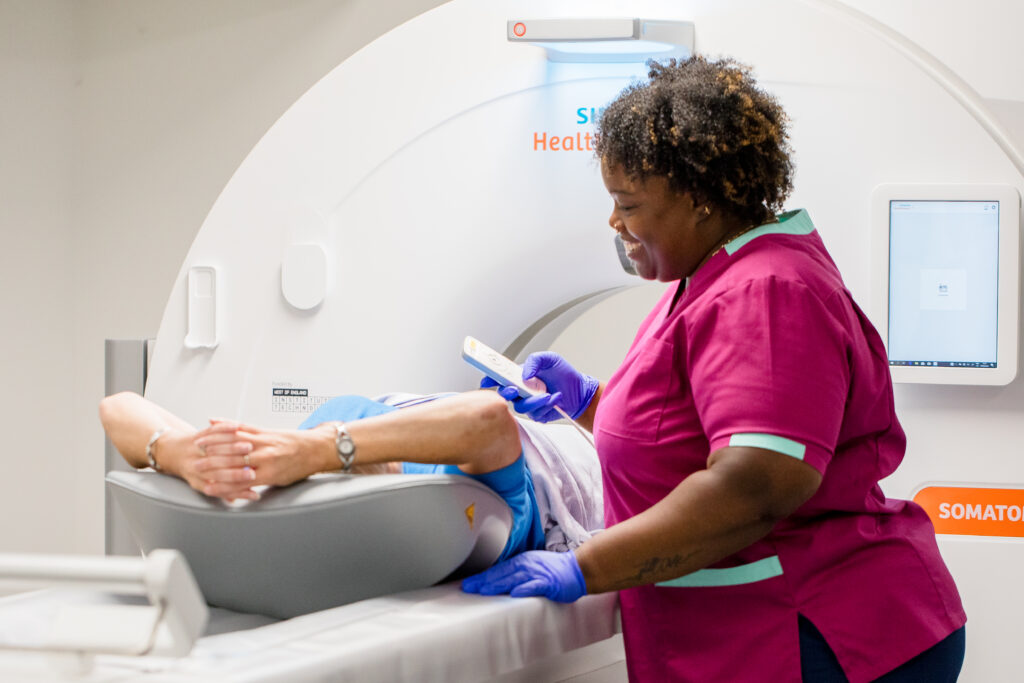
Therapeutic radiographer
Therapeutic radiographers are registered healthcare professionals who use precise doses of radiation to treat cancer and other conditions. They work as part of a multi-disciplinary team to plan and deliver personalised radiotherapy treatments using advanced imaging and technology, combining technical expertise with patient care.
To become a therapeutic radiographer, you must complete an approved undergraduate degree, a master’s in therapeutic radiography or undertake a degree apprenticeship. Once qualified, you must register with the Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) to practice.
For further information, visit:
NHS careers